Understanding Tooth Decay and Cavities
Understanding Tooth Decay and Cavities
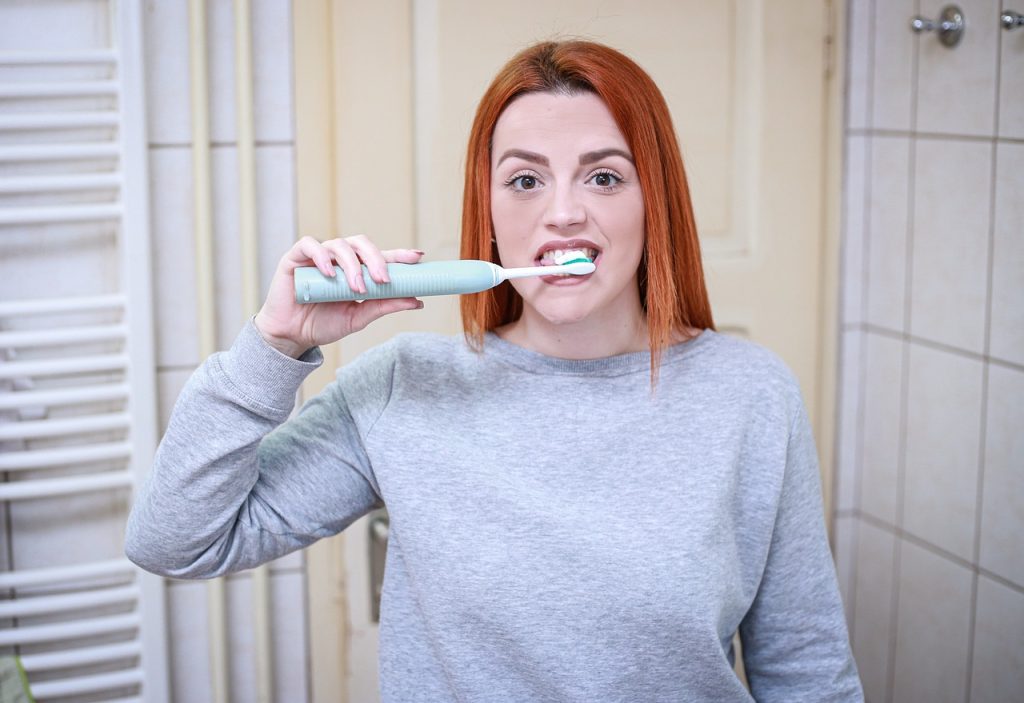

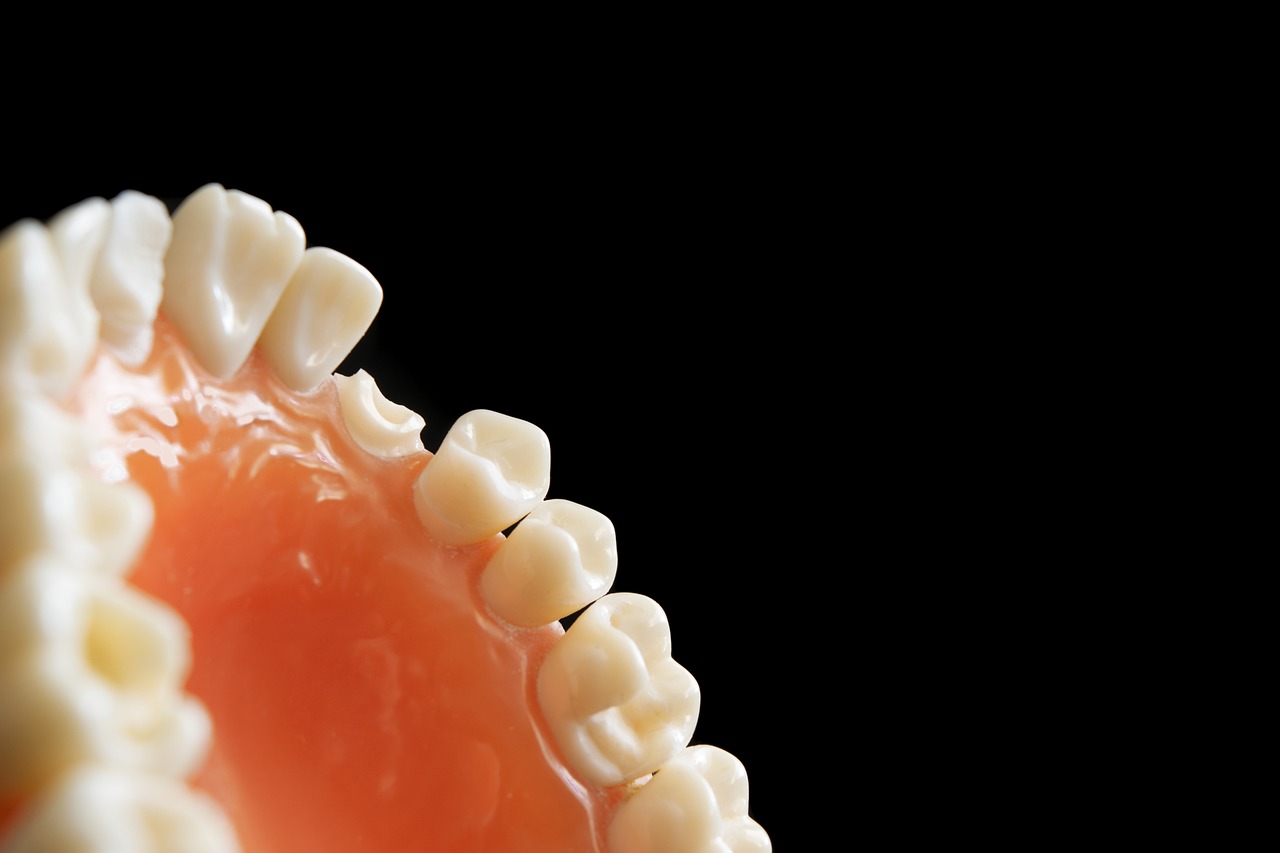
Tooth decay begins when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that attack the enamel, the tooth’s protective surface. This process can eventually lead to the formation of cavities, which are holes in the teeth. If left untreated, tooth decay can cause pain, infections, and ultimately, tooth loss.
People of all ages are susceptible to tooth decay, from children to seniors. Young children are particularly vulnerable to “early childhood caries,” also known as baby bottle tooth decay, which starts with severe decay in the front teeth and can progress to the back teeth.
For older adults, receding gums increase the risk of decay on the exposed root surfaces of teeth. This occurs when decay-causing bacteria come into contact with the tooth roots due to gum recession.
A cavity manifests as a hole in the tooth, often identified by white or dark spots on the tooth surface or sensations felt with the tongue. Early detection of cavities is crucial to prevent further complications. Regular dental check-ups can help catch decay early when treatment options are less invasive, such as fluoride treatments or simple fillings.
Maintaining good oral hygiene and being aware of early signs of tooth decay can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing cavities and the need for extensive dental procedures.
Causes of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is primarily caused by the interaction of decay-causing bacteria in
the mouth with sugars and starches from food and drinks. When these bacteria
feed on sugars, they produce acids that attack the enamel of the teeth, leading
to mineral loss. This initial stage may manifest as white spots on the enamel,
indicating early decay that can potentially be reversed with proper oral care and
fluoride use. However, if the process continues unchecked, more minerals are lost,
weakening the enamel and eventually forming cavities. Plaque, a sticky film of
bacteria, plays a crucial role in this process by facilitating acid production and
adhering to teeth, which can harden into tartar if not removed by a dental
professional. Factors such as dry mouth, genetic predisposition, inadequate oral
hygiene, and certain medical conditions like acid reflux can increase the risk of
developing tooth decay and cavities, underscoring the importance of regular
dental care and dietary moderation to maintain oral health.
Symptoms
Symptoms of tooth decay can vary depending on its stage of progression. In the
early stages, there may be no noticeable symptoms. As decay advances, common
signs include tooth sensitivity to sweet, hot, or cold foods, as well as persistent
toothaches ranging from mild discomfort to sharp pain. Visual indicators such as
holes or pits in the teeth, and discoloration (brown, black, or white stains) may
also appear. Additional symptoms can include bad breath, loose fillings, difficulty
biting certain foods, and the presence of abscesses characterized by facial
swelling, pain, or fever. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely dental
intervention to prevent further damage and complications.
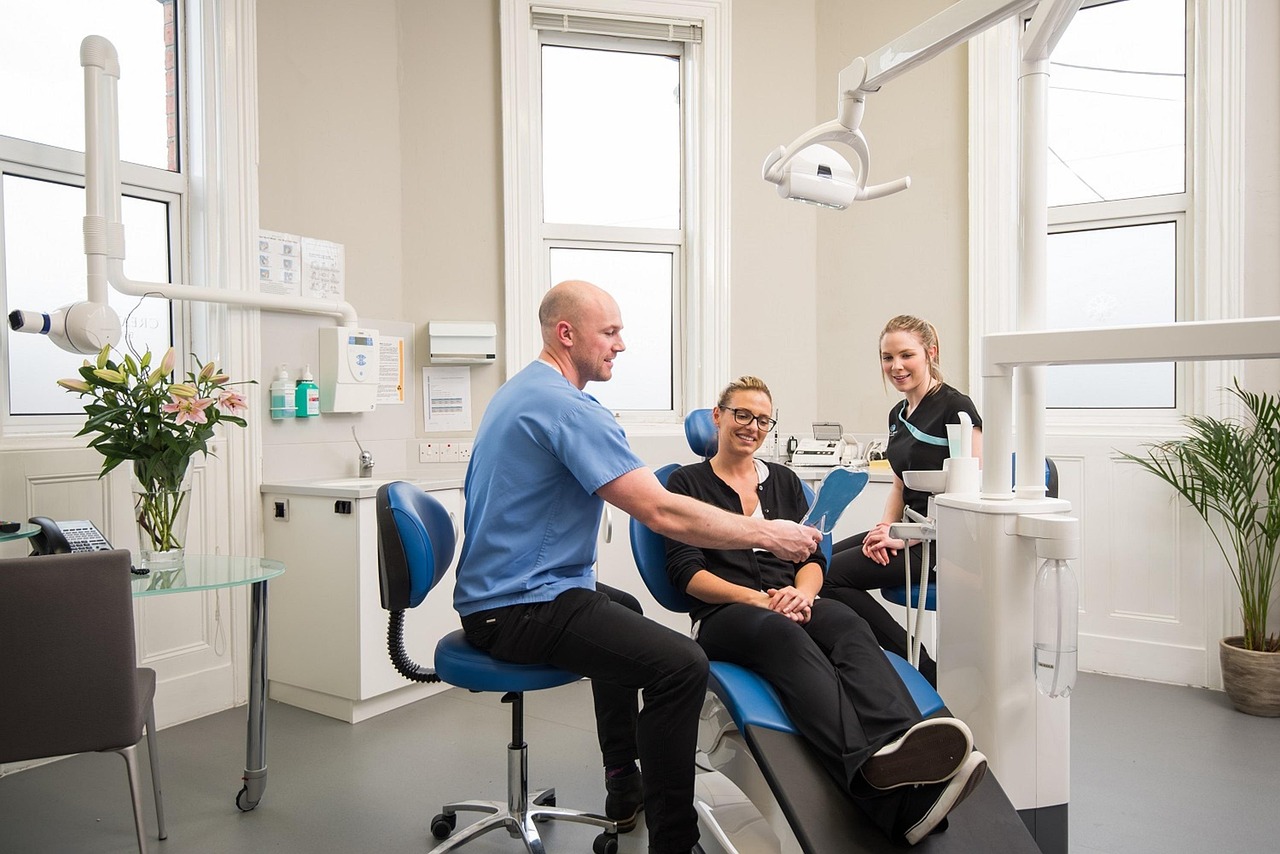
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is typically diagnosed during routine dental check-ups, where signs
like white, brown, or black staining on the tooth surface may indicate early decay.
Advanced decay may result in visible holes or cavities. Dentists can also detect
decay by identifying soft or sticky areas on the teeth or using X-rays for deeper
assessment.
Treatment options for tooth decay vary based on its severity:
- Fluoride Treatments: In the early stages of decay, fluoride application can
help remineralize enamel and potentially reverse the decay process. - Fillings: Once a cavity forms, dentists commonly treat it by removing the
decayed tissue and filling the tooth with materials like composite resin, porcelain,
or dental amalgam. - Crowns: For extensive decay or weakened teeth, crowns may be necessary
to cover and protect the tooth. Crowns can be made from various materials and
are custom-fitted to ensure durability and functionality. - Root Canals: When decay reaches the pulp of the tooth, causing infection or
severe damage, a root canal treatment is performed. This involves removing the
infected pulp, cleaning the area, and filling it to prevent further infection. - Tooth Extractions: In cases where the tooth cannot be restored, extraction
may be necessary to prevent further complications. Options to replace the
extracted tooth include dental implants or bridges to maintain dental function
and appearance.
Early intervention and regular dental visits are crucial to prevent the progression
of tooth decay and ensure optimal oral health. Seeking prompt dental care can
often mitigate the need for more invasive treatments and preserve natural teeth
effectively.
Notifications
- Dental awareness Camp at Kavisha Atria, ShelaDENTISTIUM Multispeciality Dental Clinic is organizing a Free Dental Health …
- Eminent Research Award 2025Dentistium Multispeciality Dental Clinic Wins Global Healthcare Award 2025! “Most …
- Article published on PR NEWS Network on Republic DayArticle published on PR NEWS Network on Republic Day . …
Read More "Article published on PR NEWS Network on Republic Day"
- Eminent Research Award 2024Dentistium Multispeciality Dental Clinic Honored with Health Care Icon Award …
- Dental awareness Camp at MAHER HOMES-2, Shela – 15th June 2025 –Dental Awareness Event at MAHER HOMES-2, Shela – 15TH June …
Read More "Dental awareness Camp at MAHER HOMES-2, Shela – 15th June 2025 –"
Recent Posts
- Dental Implants: Procedure, Purpose & Benefits
 Dental Implants: Procedure, Purpose & Benefits When it comes to …
Dental Implants: Procedure, Purpose & Benefits When it comes to … - The Many Factors Influencing Patient Hygiene Practices
 The Many Factors Influencing Patient Hygiene Practices Maintaining proper hygiene …
The Many Factors Influencing Patient Hygiene Practices Maintaining proper hygiene …Read More "The Many Factors Influencing Patient Hygiene Practices"
- Enhance Your Smile with Dental Crowns: A Complete Guide
 Enhance Your Smile with Dental Crowns: A Complete Guide Your …
Enhance Your Smile with Dental Crowns: A Complete Guide Your …Read More "Enhance Your Smile with Dental Crowns: A Complete Guide"
- June 2025 (6)
- May 2025 (53)
- April 2025 (2)
- March 2025 (3)
- January 2025 (2)
- November 2024 (1)
- April 2024 (1)
15,800 hits
.
Most Searched Pharmacy products on our site
-
-
-
₹2,450.00Rated 0 out of 5
Experience powerful oral care with the PRO200V PORCLEAN Water Flosser....
-
.
.









































 Lux Fresh Glow Plus Soap (150gm)
Lux Fresh Glow Plus Soap (150gm)